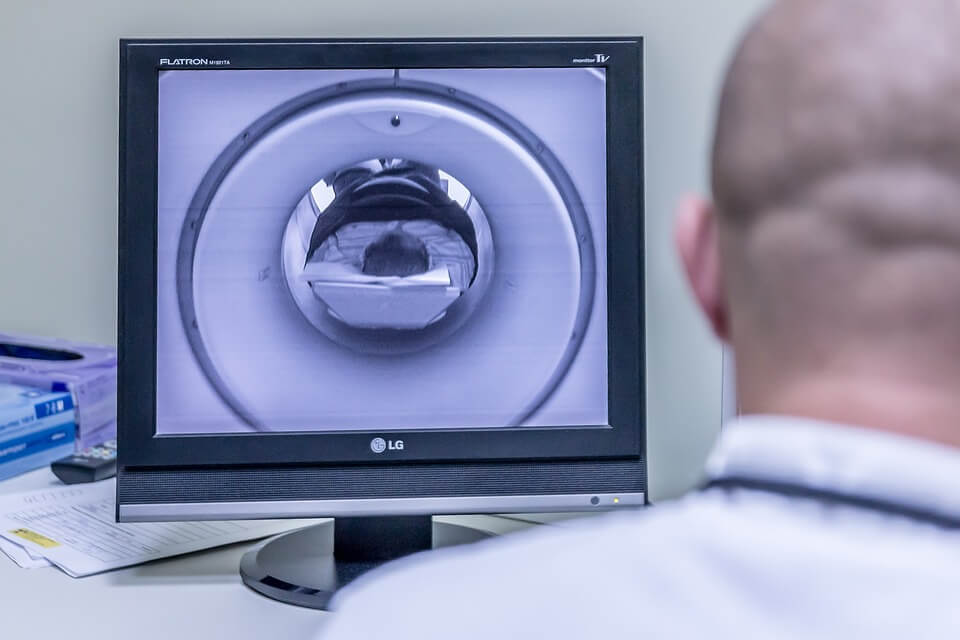
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is a medical imaging technique that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the inside of the body. It is a non-invasive procedure that does not use ionizing radiation (such as X-rays) and is considered to be a safe and painless way to diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions. The images generated by an MRI scan are highly detailed and can help doctors identify a wide range of conditions, including tumors, injuries, and diseases of the brain, spine, and internal organs. MRI can be performed in both inpatient and outpatient centers and usually needs a referral from a doctor.
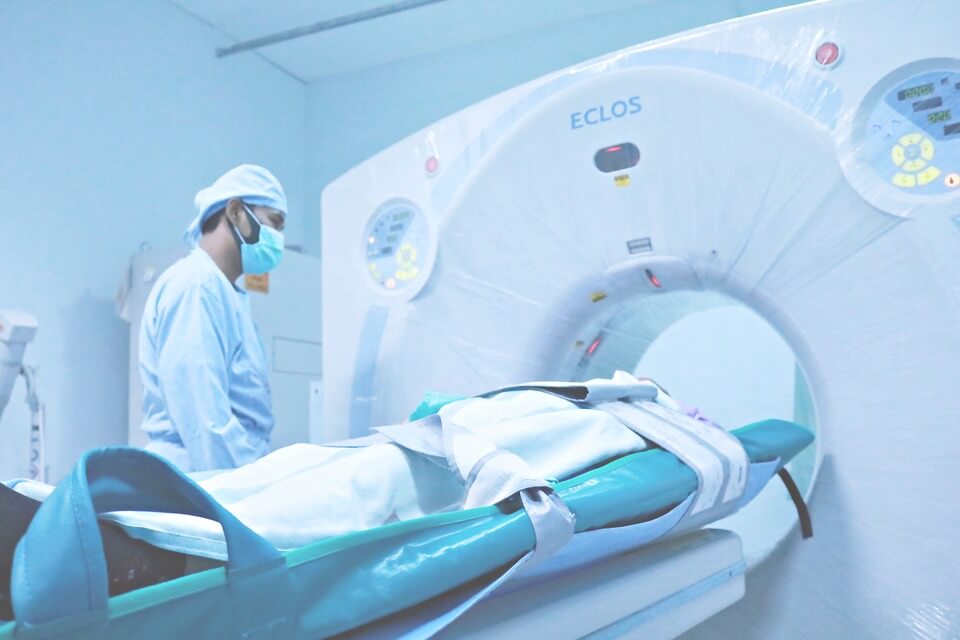
A CT (computed tomography) scan, also known as a “CAT scan,” is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. It is a non-invasive procedure that is considered to be a safe and painless way to diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions. The images generated by a CT scan are highly detailed and can help doctors identify a wide range of conditions, including tumors, injuries, and diseases of the brain, spine, and internal organs. CT scans can be performed in both inpatient and outpatient centers and usually needs a referral from a doctor.
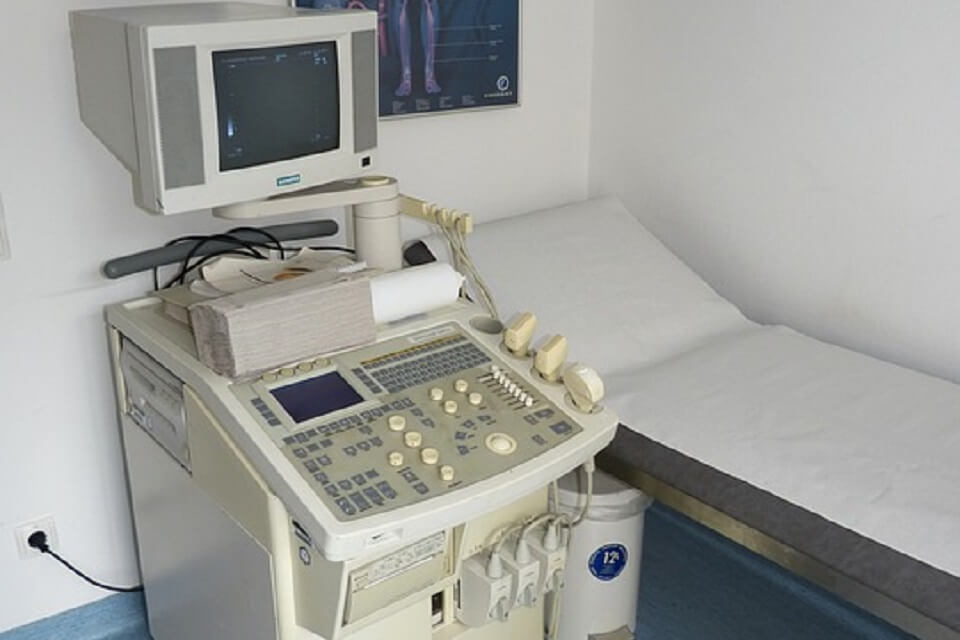
Ultrasound, also known as a sonogram, is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It is a non-invasive procedure that is considered to be safe, painless, and does not use ionizing radiation. Ultrasound is often used to visualize the internal organs, such as the liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, and kidneys. It’s also commonly used to examine the female reproductive system and to monitor the growth and development of a fetus during pregnancy. It is widely used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions, including tumors, cysts, and other abnormalities.
Fluoroscopy is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to produce real-time, moving images of the inside of the body. It is a type of X-ray imaging that allows doctors to see the internal organs and structures in motion, rather than as a single, static image. Fluoroscopy is used for a variety of procedures, such as gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract procedures, such as barium swallow, esophagogram, upper GI and lower GI series, cystography, and urethrography, as well as for interventional procedures such as angiography and biopsies. It is considered to be a safe and painless procedure, but because it uses ionizing radiation, it should only be used when the benefits outweigh the potential risks.
Cardiac scoring, also known as a coronary artery calcium (CAC) score, is a medical imaging test that uses a specialized type of CT scan to create detailed images of the coronary arteries. These are the blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle. The test is used to detect the presence of calcium deposits in the coronary arteries, which can indicate the presence of atherosclerosis (a buildup of plaque in the arteries). CAC score is usually used as a screening tool to identify people with high risk of heart disease, but it is not diagnostic of heart disease, it’s used in combination with other risk factors and clinical evaluation.
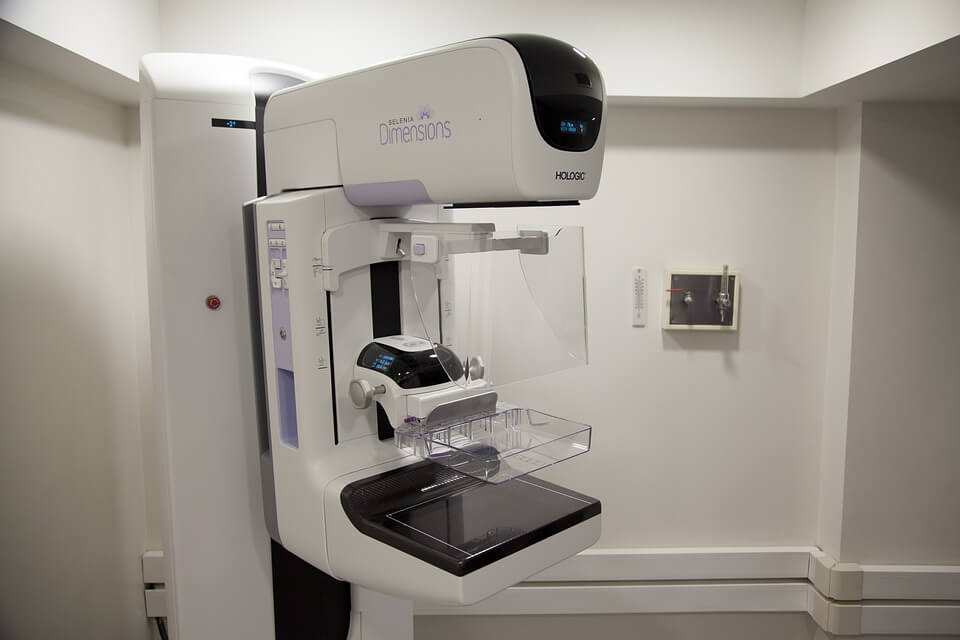
Mammography is a medical imaging test that uses low-dose X-rays to create detailed images of the breast tissue. It is used to detect and diagnose breast cancer, as well as to monitor changes in the breast tissue over time. Mammography is considered to be one of the most effective tools for detecting breast cancer in its early stages, when it is most treatable. There are two types of mammography: digital mammography and film mammography. Digital mammography uses a digital detector to capture the images, while film mammography uses traditional X-ray film. It is usually recommended for women over the age of 50 and women with a family history of breast cancer. It can detect lumps or abnormalities that may not be visible or palpable.